South Korea Bike Sharing Market Size, Share, Growth Trends, Industry Analysis, Key Players, Investment Opportunities and Forecast (2025-2032)
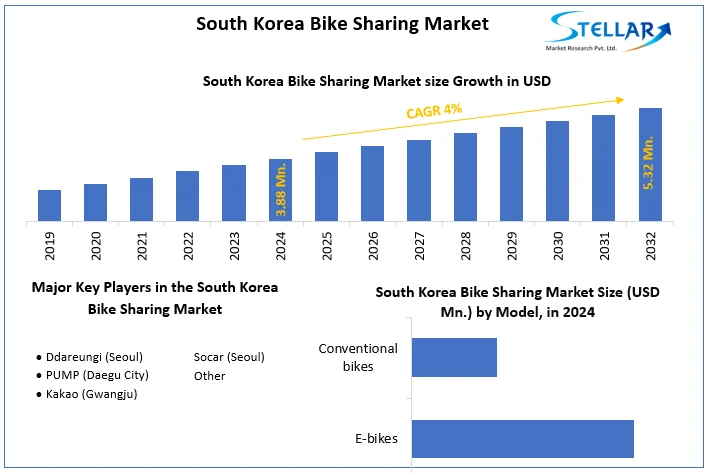
South Korea Bike Sharing Market size was valued at US$ 3.88 Million in 2024 and the total South Korea Bike Sharing Market revenue is expected to grow at 4% through 2025 to 2032, reaching nearly US$ 5.32 Million.
Format : PDF | Report ID : SMR_252
South Korea Bike Sharing Market Overview:
South Korea ranks 6th in APAC in bike sharing with 28% YOY growth as new technologies for bike sharing are emerging in the main city Seoul and other regions. Moreover, people are adopting the healthy lifestyle over other which is considered to drive the market growth in the region.
South Korea Bike Sharing Market Dynamics:
In addition to a series of safety and maintenance measures, the city of Seoul has introduced a new service for users of the Ttareungyi public bicycle sharing service. App-based bicycle-sharing services in the city have become a popular personal mode of transportation during the coronavirus pandemic as people avoid crowded public transport such as trains and buses. The number of Ttareungyi users increased by 24% year-on-year to 2.78 million in 2020. The city government said the new measures are aimed at preventing potential breakdowns and accidents, as the number of bicycle rentals has also reached 23.7 million, up 14% year-on-year. Reflective strips and reflectors have been added to the bike to give riders and pedestrians a better view of the bike at night.
Approximately 3,000 new bicycles introduced this year or requiring replacement of old tires will initially be affected by this measure. This plan reflects the opinion of many citizens that 38% of bicycle use occurs after 6 pm, so the more prominent the Ttareungyi bicycle at night, the more convenient and safe it will be. Until 6 am last year. Chain tensioners and chain guards are installed on 400 bicycles for test runs to prevent the bicycle chain from coming off the wheels and leading to an accident. By October, more lights are expected to be installed in 254 rental sites in dark places with insufficient streetlights.
To get more Insights: Request Free Sample Report
A smaller version of the Ttareungyi bike will also be prepared for people shorter than 160 centimeters. This smaller version will be available for children aged as young as 13, who can register for the service with their parents` approval, while the regular Ttareungyi is available for people aged 14 and over. For 13yearolds, they will be able to use the service after watching a 30second safety guide video on the app. The city government has also updated the app for the service recently. It has diversified login and payment methods to shorten the time needed for the process. We also added Chinese and Japanese to the previous language options for Korean or English. In addition to the six centers currently in operation, we plan to open a maintenance center in the southeast of the city this year. At the rental station, simple maintenance such as tire pressure adjustment can be performed quickly.
Price Trends in South Korea Bike Sharing:
|
Category |
Season Pass |
One-day Pass (member) |
One-day Pass (non-member) |
|
Products |
|
|
|
|
Payment |
Mobile phone, credit card, |
Mobile phone, credit card, |
Mobile phone, credit card |
|
Additional Fees |
General pass - Additional charge of KRW 1,000 for every additional 30 minutes Premium pass - Additional charge of KRW 1,000 for every additional 30 minutes |
||
|
Hours |
[General pass] Rental time: 60 minutes [Premium pass] Rental time: 120 minutes Additional charges will incur when the bicycle is not returned within the rental time (60 minutes). Failure to pay the additional charges will result in suspension of services. When not returned within the rental time (4 hours for general pass and 6 hours for premium pass), the bicycle will be considered to have been stolen or lost. |
||
Seoul City- New Hotspot for bike sharing in South Korea
The bicycle-sharing program in Seoul, the capital of South Korea, produces more than 1 million rides a month, with more than 1,500 bicycle-sharing stations and about 20,000 bicycles operating in the city. Examine the spatial patterns of bike-sharing use in Seoul, a highly populated city with a large subway system. A negative binomial conditional autoregressive model that explains spatial correlation is used to analyze the relationship between land use, subway stations, employment density, population density, and bike share use. For all models, the results show a positive correlation between bike share usage and the number and employment density of subway stations, with the former having a greater impact. Land use for agriculture and entertainment is negatively associated with bicycle use in many models. It also examines different types of trips to distinguish between "round trips" (starting and ending at the same station) and target trips between the two destinations. The former shows a pattern that suggests that "round trip" is a more leisure trip.
South Korea's ride-sharing company said its business is booming as bicycle sharing is gaining popularity as a form of green transport amid growing concerns about air pollution. In South Korea, automobile exhaust is considered to be one of the main causes of air pollution. If the city government declares emergency measures to reduce particulate matter levels, some vehicles containing harmful pollutants may be banned from driving in Seoul. The two companies also emphasize that the service is far more user-friendly than the service provided by the municipality, as users do not have to look for a parking space after renting a bicycle. For example, cocoa users can use the cocoa T app to see where their bike is before using it. One can return the bicycle to a place that you think is appropriate, such as a highway, an underground parking lot, or a building entrance.
New Product Launches:
South Korea's largest telecommunications company, KT, has launched a bicycle rental service in collaboration with domestic mobility service companies, reflecting the growing popularity of eco-friendly services in cities such as Seoul. “Ttareungi”, a public bicycle sharing service launched by the city of Seoul in 2015, is Korea's first and most successful mobility sharing business model. In 2020, about 37,000 bicycles were used more than 23.7 million times, 24% more than a year ago. The fare is 1,000 won ($ 0.88) per hour.
KT aggressively expands its service area in Seoul's satellite city to domestic competitors such as Kakao Mobility, which evaluated Seoul's services for the launch of Kakao T Bike, an electric bicycle mobility service in 2019. The local government has launched a competitive bicycle sharing service. In a statement on March 15, KT partnered with Omni system, the developer of intelligent platform solutions, and Goyang, a satellite city in northwestern Seoul, to launch 400 units near subway stations and densely populated areas. "Tazo" said it has released a bicycle. The mobility service will be available free of charge until April 11th.
Approximately 1,000 bicycles will be added on April 12, and full service will be provided for a fee of 500 won per 20 minutes. Tazo was first deployed in October in Suwon, southern Seoul. Unlike other services, users do not have to return their bike to a particular station. Workers take their bicycles out at night and use them in subway stations and other crowded areas. Suwon drives about 3,000 Tazo bikes. KT has diversified its mobility services through a multifaceted strategy. In 2019, the company partnered with domestic motorcycle manufacturer Daelim Motorcycle and motorcycle rental company AJ Bike to develop an electric scooter rental business model for courier and food delivery companies.
After investing in Nine2One, Socar plans to launch its own bike sharing service in Seoul by the end of this month. According to the company, it will provide 350 bicycles as an initial service and expand to 2,000 bicycles nationwide.
New Market Entrants are joining the Heat:
Ride-sharing companies in South Korea are expanding their business portfolio to include sharing electric bicycles, and high expectations are rising as local governments are scrambling to introduce services that replace traditional transportation. Cacao, the largest messenger app company in Japan, has entered the electric bicycle sharing business with a new service called Cacao T-Bike. The company started operations in Incheon and Jonan, Gyeonggi Province on March 6.
Seoul-based car-sharing startup Socar has also joined the push by investing in emerging electric bike sharing service provider Nine2One. The company announced that it will launch a shared service later this month. The bicycle sharing business, whether traditional or electric, is at the center of fierce competition nationwide. Since March last year, the government has allowed electronic bicycles to be carried in the lane with ordinary cars. Inspired by the success of similar ventures in Seoul, some of the surrounding communities, such as Seongnam and Suwon, have joined the global bike-sharing platform.
Seoul has been operating a bicycle sharing service since 2015. Bicycles are available at designated locations throughout Seoul. Currently, the Seoul government has released about 20,000 people. The Seoul Metropolitan Government said, "The number of bicycles (available for shared services) is 20 per 10,000 residents of Seoul." “Most of them are more than 20 meters away from subway and bus stations.” In Suwon, about 5,000 bicycles have been used as part of a shared service since the program started in January last year. The city government is working with Singapore-based bicycle sharing company Obike. Jonan also started a similar bicycle sharing service in cooperation with cacao. About 600 electric bicycles are part of the service. About 400 cacao bicycles are in operation at Matsushima in Incheon.
The objective of the report is to present a comprehensive analysis of the South Korea Bike Sharing Market to the stakeholders in the industry. The report provides trends that are most dominant in the South Korea Bike Sharing Market and how these trends will influence new business investments and market development throughout the forecast period. The report also aids in the comprehension of the South Korea Bike Sharing Market dynamics and competitive structure of the market by analyzing market leaders, market followers, and regional players.
The qualitative and quantitative data provided in the South Korea Bike Sharing Market report is to help understand which market segments, regions are expected to grow at higher rates, factors affecting the market, and key opportunity areas, which will drive the industry and market growth through the forecast period. The report also includes the competitive landscape of key players in the industry along with their recent developments in the Bike Sharing Market. The report studies factors such as company size, market share, market growth, revenue, production volume, and profits of the key players in the South Korea Bike Sharing Market.
The report provides Porter's Five Force Model, which helps in designing the business strategies in the market. The report helps in identifying how many rivals are existing, who they are, and how their product quality is in the Market. The report also analyses if the South
Korea Bike Sharing Market is easy for a new player to gain a foothold in the market, do they enter or exit the market regularly if the market is dominated by a few players, etc.
The report also includes a PESTEL Analysis, which aids in the development of company strategies. Political variables help in figuring out how much a government can influence the Market. Economic variables aid in the analysis of economic performance drivers that have an impact on the Market. Understanding the impact of the surrounding environment and the influence of environmental concerns on the South Korea Bike Sharing Market is aided by legal factors.
South Korea Bike Sharing Market Scope:
|
South Korea Bike Sharing Market |
|
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 3.88 Mn. |
|
Market Size in 2032 |
USD 5.32 Mn. |
|
CAGR (2025-2032) |
4% |
|
Historic Data |
2019-2024 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Segment Scope |
By Model
|
|
By Model
|
|
|
|
By Sharing System
|
South Korea Bike Sharing Market Players:
Frequently Asked Questions
Seoul, Busan, and Gwangju region have the highest growth rate in the South Korea Bike Sharing market.
Ddareungi, Socar, PUMP are the key players in the South Korea Bike Sharing market.
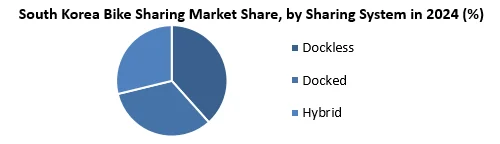
Docked sharing segment is dominating the market with highest share owing to abundance of docking stations in the metro regions of South Korea owing to smart city initiative by government.
1. South Korea Bike Sharing Market: Research Methodology
1.1. Research Process
1.1.1. Primary Data
1.1.2. Secondary Data
1.2. Market Size Estimation
1.2.1. Bottom-Up Approach
1.2.2. Top-Down Approach
1.3. Market Breakdown and Data Triangulation
1.4. Research Assumption
2. South Korea Bike Sharing Market Introduction
2.1. Study Assumption and Market Definition
2.2. Scope of the Study
2.3. Executive Summary
3. South Korea Bike Sharing Market: Competitive Landscape
3.1. Stellar Competition Matrix
3.2. Key Players Benchmarking
3.2.1. Company Name
3.2.2. Business Segment
3.2.3. End-user Segment
3.2.4. Revenue (2024)
3.2.5. Company Locations
3.3. Market Structure
3.3.1. Market Leaders
3.3.2. Market Followers
3.3.3. Emerging Players
3.4. Mergers and Acquisitions Details
4. South Korea Bike Sharing Market: Dynamics
4.1. Market Trends
4.2. Market Driver
4.3. Market Restraints
4.4. Market Opportunities
4.5. Market Challenges
4.6. PORTER’s Five Forces Analysis
4.7. PESTLE Analysis
4.8. Technological Roadmap
4.9. Regulatory Landscape
5. South Korea Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast by Segments (by Value in USD Million)
5.1. South Korea Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Bike Type (2024-2032)
5.1.1. E-bikes
5.1.2. Conventional bikes
5.2. South Korea Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Model (2024-2032)
5.2.1. Free-floating
5.2.2. P2P
5.2.3. Station based
5.3. South Korea Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Sharing System (2024-2032)
5.3.1. Dockless
5.3.2. Docked
5.3.3. Hybrid
6. Company Profile: Key players
6.1. Ddareungi (Seoul)
6.1.1. Company Overview
6.1.2. Financial Overview
6.1.3. Business Portfolio
6.1.4. SWOT Analysis
6.1.5. Business Strategy
6.1.6. Recent Developments
6.2. PUMP (Daegu City)
6.3. Kakao (Gwangju)
6.4. Socar (Seoul)
6.5. Others
7. Key Findings
8. Industry Recommendations
















