Japan Bike Sharing Market Industry Overview, Size, Share, Growth Trends, Research Insights and Forecast (2025–2032)
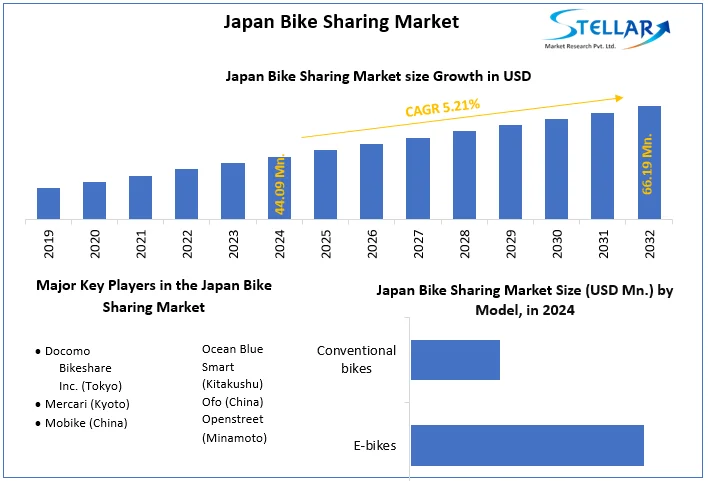
Japan Bike Sharing Market size was valued at US$ 44.09 Million in 2024 and the total Japan Bike Sharing Market revenue is expected to grow at 5.21% through 2025 to 2032, reaching nearly US$ 66.19 Million.
Format : PDF | Report ID : SMR_227
Japan Bike Sharing Market Overview:
Bicycles play a major role in the world as an economical, effective and environmentally friendly means of transportation. The modal share of bicycles is about 25% in Osaka and about 14% in Tokyo, which is much higher in Japan than in many EU countries. On average, there is one bicycle for every 1.5 people in Japan, making Japan one of the largest cycling countries. Osaka has the highest bicycle modal share at about 25%. There are about 8.4 million bicycles in Tokyo, the modal share of bicycles in the 23 wards of Tokyo is about 10%, and 18% of railway users arrive at the station by bicycle.
Japan Bike Sharing Market Dynamics:
As of October 2020, there are 100 cities in Japan where the public bicycle system (included in the pilot program) is available. The number of ports in Japan exceeds 10 (up to 44). It shows that the range of the public bicycle system in Japan is small compared to other countries. The "Bicycle Parking Facility Development Guidelines" published by MLITT mentions the promotion and popularization of public bicycle systems. The reason the bicycle parking policy talks about public bicycles is that many cities started bicycle parking systems many years ago by saving bicycles or parking illegal bicycles. But today, many cities are installing public bicycles to improve the transportation network connected to public transport stations.
To get more Insights: Request Free Sample Report
Japanese cities only host small PBSPs, but show high usage of private bicycles (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism [MLIT]). Implementing PBSP in Japan involves many challenges, such as the difficulty of raising funds for implementation and the determination of the optimal business model for operation. Some of these issues are due to a shortage of full-time operators, limited operating conditions and budgets. Therefore, there is an urgent need to address the lack of continuity of PBSP operations in Japan. In particular, it is essential to continue to manage programs that are relatively small but strategically placed for easy access. At the same time, project evaluation requires cost-benefit analysis and profitability analysis to ensure the sustainable operation of the PBSP.
The Japan Bicycle Promotion Association has calculated the initial and ongoing operating costs of small PBSPs in Japan. It turned out that the cost of Yokohama city in Japan is 5 million yen (US $ 54,348) per dock. This number includes patrol personnel, bicycle transportation, bicycle equipment repair, system use, membership management, electricity and communications charges, and business management costs. Each of these costs (depending on the number of dock stations installed at your site) is required as part of the operating costs of PBSP. The City of Minneapolis is a medium-sized PBSP with facilities derived from 1,000 bicycles, 50 solar kiosk, 1,500 kiosk bicycle racks, 394 kiosk platforms, and 15,950 system cards. We have decided that the total cost will be $ 3,200,475. .. The city details and itemizes its operating costs, which primarily comprise annual costs related to personnel expenses (265,064 USD), maintenance car and equipment loans (22,764 USD), and maintenance contract fees (248,616 USD). In addition to these expenses, the program in Minneapolis also costs an additional 31,150 USD for other maintenance expenses and 212,444 USD for overhead costs such as communications and office rent.
Comparison of Japanese PBSC Business Scales with other Countries:
So far, the government has played a passive role and is more dependent on private investment, which has been successful with only a few counts. The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs suggests that increasing government investment in pilot projects may help determine the best financial model for building and maintaining a PBS system in Japan. More commuting to create the right end-to-end PBS system to attract and maintain riders, focus on ensuring safety, identify suitable areas for cycling, and experiment with innovative customer acquisition models. You also need to take a person-centric approach.
Public Bicycle-Sharing Projects and Users in Japan:
In Japan, bicycle sharing pilot projects are being implemented in many cities and regions such as Kitakyushu City, Setagaya Ward (Tokyo), Sapporo City, Hiroshima City, Nagoya City, Hanshin Area, Chigasaki City, Okayama City, Sendai City, and Kanazawa City. It has been. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT)) organized the characteristics of each pilot project and summarized the characteristics through a questionnaire survey of users. Table 4 and Figures 1 and 2 outline some of the projects. The Japanese pilot project used 50-300 bicycles. It's significantly smaller than the approximately 20,000 bikes in Paris and the 6,000 bikes in London. Bicycle and daily usage was a minimum of 0.22 and a maximum of almost 6. Each use was very different. However, with the exception of Nagoya and Sendai, bicycles were commonly used for sightseeing.
In Sendai and Nagoya, most of them were used for shopping. On the other hand, except for Nagoya and Sendai, there were not many business uses. Especially in the case of Nagoya, the pilot project has enabled unique characteristics such as other characteristics in addition to being relatively large in relation to the area where the project was carried out. The conversion rate of public transportation such as buses and trains is generally high. There were not many car modifications that were expected to have a positive impact on the environment and health. According to official Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism sources, and more than 70 cities did not formally pilot in 2019, but fully implemented PBSP. Especially in Tokyo, the number of PBSPs is increasing rapidly.
Kitakyushu Project Case Study:
To use the undertaking, customers want to end up registered participants. Members pay 525 yen month-to-month because the base price. The charge is one hundred and five yen in line with hour for real utilization, and the most price in line with day is 525 yen. Aside from the hourly price, customers can pick out a month-to-month price machine. By paying 5,250 yen, they are able to use the undertaking as usually as they prefer at some stage in a month. In addition, assuming there is probably non-registered travelers or transient commercial enterprise-use customers, the undertaking gives a 1-day person machine for non-registered participants. By paying 500 yen, human beings can use the bicycles as usually as they need at some stage in a day. If customers need to apply each the automobile-sharing and public bicycle sharing services, they need to pay the initiation charge for the automobile sharing and the bicycle utilization charge as well.
However, the price approach and the machine are artificial in order that each may be effortlessly used. As of December 31, 2020, the general public bicycle-sharing undertaking had reached 30 registered organization participants (604 folks) and 500 people registered participants, for 865 registered participants overall, demonstrating an upward trend. The each day imply utilization remember numerous relying at the month. The overall quantity of each day utilization changed into typically 50 to eighty times. The usage charges in line with bicycle in line with day had been 0.43–0.69. The outcomes are just like the ones of the Hiroshima City undertaking, as are the sizes of the 2 projects. The Kitakyushu municipal authorities officials` legit commercial enterprise use of the general public bicycle-sharing undertaking is covered withinside the company member use. To sell low-carbon network building, public officials took the initiative in the use of the undertaking. They had used it because September 2010. The quantity of registered participants changed into 38 sections, for 366 folks in overall, accounting for about 40% of the overall.
The objective of the report is to present a comprehensive analysis of the Japan Bike Sharing Market to the stakeholders in the industry. The report provides trends that are most dominant in the Japan Bike Sharing Market and how these trends will influence new business investments and market development throughout the forecast period. The report also aids in the comprehension of the Japan Bike Sharing Market dynamics and competitive structure of the market by analyzing market leaders, market followers, and regional players.
The qualitative and quantitative data provided in the Japan Bike Sharing Market report is to help understand which market segments, regions are expected to grow at higher rates, factors affecting the market, and key opportunity areas, which will drive the industry and market growth through the forecast period. The report also includes the competitive landscape of key players in the industry along with their recent developments in the Bike Sharing Market. The report studies factors such as company size, market share, market growth, revenue, production volume, and profits of the key players in the Japan Bike Sharing Market.
The report provides Porter's Five Force Model, which helps in designing the business strategies in the market. The report helps in identifying how many rivals are existing, who they are, and how their product quality is in the Market. The report also analyses if the Japan Bike Sharing Market is easy for a new player to gain a foothold in the market, do they enter or exit the market regularly if the market is dominated by a few players, etc.
The report also includes a PESTEL Analysis, which aids in the development of company strategies. Political variables help in figuring out how much a government can influence the Market. Economic variables aid in the analysis of economic performance drivers that have an impact on the Market. Understanding the impact of the surrounding environment and the influence of environmental concerns on the Japan Bike Sharing Market is aided by legal factors.
Japan Bike Sharing Market Scope:
|
Japan Bike Sharing Market |
|
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 44.09 Mn. |
|
Market Size in 2032 |
USD 66.19 Mn. |
|
CAGR (2025-2032) |
5.21% |
|
Historic Data |
2019-2024 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Segment Scope |
By Model
|
|
By Model
|
|
|
|
By Sharing System
|
|
Regional Scope |
North America- United States, Canada, and Mexico Europe – UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Austria, and Rest of Europe Asia Pacific – China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, ASEAN, Rest of APAC Middle East and Africa - South Africa, GCC, Egypt, Nigeria, Rest of the Middle East and Africa South America – Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America |
Japan Bike Sharing Market Players:
- Docomo Bikeshare Inc. (Tokyo)
- Mercari (Kyoto)
- Mobike (China)
- Ocean Blue Smart (Kitakushu)
- Ofo (China)
- Openstreet (Minamoto)
Frequently Asked Questions
Tokyo, Minamoto, Kyoto, and Kyushu region have the highest growth rate in the Japan Bike Sharing market.
Docomo Bikeshare Inc., Mercari, Mobike, Ocean Blue Smart, Ofo, and Openstreet are the key players in the Japan Bike Sharing market.
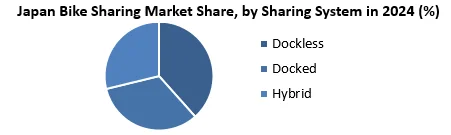
Docked sharing segment is dominating the market with highest share owing to abundance of docking stations in the metro regions of Japan owing to smart city initiative by government.
1. Japan Bike Sharing Market: Research Methodology
1.1. Research Process
1.1.1. Primary Data
1.1.2. Secondary Data
1.2. Market Size Estimation
1.2.1. Bottom-Up Approach
1.2.2. Top-Down Approach
1.3. Market Breakdown and Data Triangulation
1.4. Research Assumption
2. Japan Bike Sharing Market Introduction
2.1. Study Assumption and Market Definition
2.2. Scope of the Study
2.3. Executive Summary
3. Japan Bike Sharing Market: Competitive Landscape
3.1. Stellar Competition Matrix
3.2. Key Players Benchmarking
3.2.1. Company Name
3.2.2. Business Segment
3.2.3. End-user Segment
3.2.4. Revenue (2024)
3.2.5. Company Locations
3.3. Market Structure
3.3.1. Market Leaders
3.3.2. Market Followers
3.3.3. Emerging Players
3.4. Mergers and Acquisitions Details
4. Japan Bike Sharing Market: Dynamics
4.1. Market Trends
4.2. Market Driver
4.3. Market Restraints
4.4. Market Opportunities
4.5. Market Challenges
4.6. PORTER’s Five Forces Analysis
4.7. PESTLE Analysis
4.8. Technological Roadmap
4.9. Regulatory Landscape
5. Japan Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast by Segments (by Value in USD Million)
5.1. Japan Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Bike Type (2024-2032)
5.1.1. E-bikes
5.1.2. Conventional bikes
5.2. Japan Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Model (2024-2032)
5.2.1. Free-floating
5.2.2. P2P
5.2.3. Station based
5.3. Japan Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Sharing System (2024-2032)
5.3.1. Dockless
5.3.2. Docked
5.3.3. Hybrid
6. Company Profile: Key players
6.1. Docomo Bikeshare lnc. (Tokyo)
6.1.1. Company Overview
6.1.2. Financial Overview
6.1.3. Business Portfolio
6.1.4. SWOT Analysis
6.1.5. Business Strategy
6.1.6. Recent Developments
6.2. Mercari (Kyoto)
6.3. Mobike (China)
6.4. Ocean Blue Smart (Kitakushu)
6.5. Ofo (China)
6.6. Openstreet (Minamoto)
7. Key Findings
8. Industry Recommendations
















