China Bike Sharing Market Size, Share, Growth Trends, Industry Analysis, Key Players, Investment Opportunities and Forecast (2025-2032)
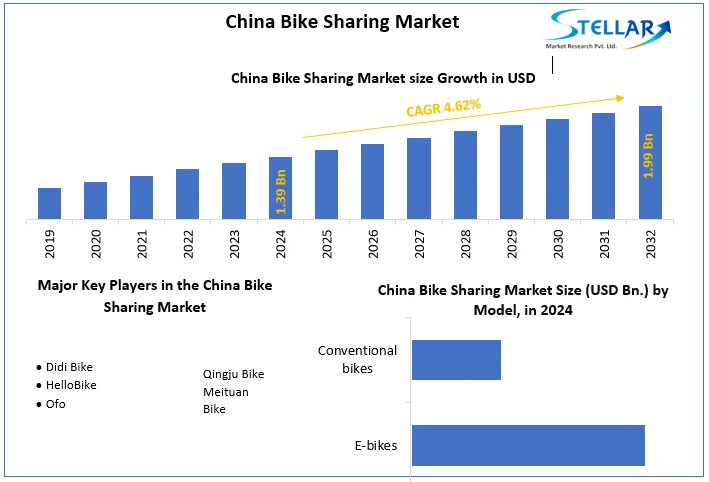
China Bike Sharing Market size was valued at US$ 1.39 billion in 2024 and the total China Bike Sharing Market revenue is expected to grow at 4.62% through 2025 to 2032, reaching nearly US$ 1.99 billion.
Format : PDF | Report ID : SMR_169
China Bike Sharing Market Overview:
In Shanghai alone, 1.5 million shared bikes were circulating in November, about 1 bike for every 16 citizens. At the end of October 2017 the number of bikes had dropped to 1.1 million because operators were forced to remove bikes that were in a poor condition. In Beijing in September 2017, 15 different operators had about 2.3 million shared bikes in the city, but the addition of further bikes has been banned. In 2024, Chinese market has showed 7.1% YOY growth and expected to register CAGR of 4.62% during the forecast period.
China Bike Sharing Market Dynamics:
Business Diversification in China Bike Sharing Market:
At the beginning of 2018 several bike sharing operators have started to further diversify their businesses in order to say afloat. One common plan is to also offer ebike sharing services in the future. In January 2018, mobike announced that it would enter the ride hailing market with a small pilot project in Guizhou. Almost at the same time, oBike became known to also offer a small delivery service under the name oBike Flash. China's regulatory compliance:
To get more Insights: Request Free Sample Report
One of the first reactions in many Chinese cities was the confiscation of a destroyed or illegally parked shared bicycle. This created a huge bicycle graveyard with thousands of shared bicycles. "In May 2019, the Ministry of Transport of China drafted the first national framework to regulate the sharing of dockless bicycles and issued a formal regulation in August 2019. The new law regulates cycling and traffic standards, imposes penalties on individuals for illegal activities, ensures equal distribution of bicycles to local governments, and requires them to provide designated parking spaces. Since then, nearly 30 Chinese cities have issued regulations that guide the manufacture, operation and maintenance of bicycle sharing in accordance with national guidelines. These cities often have stricter standards, such as: B. Annual inspection of the bicycle, minimal maintenance personnel, and operator responsibility for cleaning the bicycle (see here).
Shanghai was one of the first cities to take such city-wide measures, drafting a bill in April 2020 and issuing it in October. “The guidelines encourage local governments to integrate bicycle parking into their city planning requirements. It requires operators, government officials and agencies to control the city`s bike fleet, such as requiring bike plate registration, banning shared electric bikes, and guaranteeing better parking by using Geofence technology”. In addition, a cap is set on the maximum number of bikes allowed. “The regulation also protect consumers financially. The city appointed an independent financial institute to oversee bike users` deposits, assuring that they`ll receive their money back of a bike share operator goes bankrupt”.
Tianjin, a city known for its many bicycle producers, also quickly noticed that the oversupply of shared bikes posed a problem for the city. In May 2018, several Tianjin city authorities announced the "Tianjin Internet Rental Cycle Provisional Measures". It is a set of regulations that define the roles and responsibilities of operators, users, and the government itself. This regulation came into effect in October 2017. The regulation requires orderly parking, bicycle quality and timely maintenance, standardized data sharing with the city, transparent and safe user deposits, clear rules and enforcement.
Nanjing decided in August 2017 to introduce operator licensing requirements from 2018. In January 2018, Shenzhen banned bicycle rental company Didi Chuxing from putting Bluegogo branded bicycles on the street because bicycles and user deposits were substandard. Overall, Shenzhen has very strict regulations on bike rental companies, and recent assessments have shown that bike rental companies are often very poorly managed. To actually address the Overcapacity issue, many cities, including Shanghai, Beijing and Guangzhou, have further banned the addition of shared bicycles. In the spring of 2018, Beijing introduced an electronic fence to ensure proper parking of bicycles. Previously, a parking policy was issued, but it was not properly enforced.
Deposit Structure:
In February 2019, it was announced that the Ministry of Transport of China, the People's Bank of China and the China Banking Regulatory Commission have drafted a law regulating deposits for bicycle sharing services. The bankruptcy of a bicycle-sharing company has resulted in a loss of 1 billion yuan on user deposits, much more owned by the bicycle company. The new policy proposes three options. Operators who rent a bike without a deposit, refund the deposit immediately after returning the bike, or require a deposit must set up a separate account for the deposit under state control.
Economic Problems in China's Bicycle Sharing Market:
The dockless bicycle sharing business model does not provide economies of scale and is highly capital intensive. So far, despite the large investment, none of the Chinese operators are making a profit. There are many articles about how unsustainable the entire business model is, as it is cheaper to put in a new bike than to repair a broken bike. Therefore, many believe that the actual business model is data acquisition. This was confirmed when journalists discovered a major data breach with operator oBike in November 2017. Bicycle-sharing companies burned cash rapidly, and in December 2017, rumors emerged that ofo's cash was only $ 53 million and Mobike's cash was $ 1.86 trillion.
Each reportedly spent more than $ 466 million in deposit funds to fund the business. However, both companies have denied these claims. Bluegogo, the third largest company, went bankrupt in mid-November 2017. But this is not the only company, in 2017 five Chinese bike share operators went bankrupt and $150 million in deposits could not be refunded to users, as it seems that deposits are often used to advance the business. Due to problems with paying back deposits when an operator is going bankrupt, the Chinese Consumer Association is now asking for stricter regulations on deposits.
The objective of the report is to present a comprehensive analysis of the China Bike Sharing Market to the stakeholders in the industry. The report provides trends that are most dominant in the Bike Sharing Market and how these trends will influence new business investments and market development throughout the forecast period. The report also aids in the comprehension of the China Bike Sharing Market dynamics and competitive structure of the market by analyzing market leaders, market followers, and regional players.
The qualitative and quantitative data provided in the China Bike Sharing Market report is to help understand which market segments, regions are expected to grow at higher rates, factors affecting the market, and key opportunity areas, which will drive the industry and market growth through the forecast period. The report also includes the competitive landscape of key players in the industry along with their recent developments in the China Bike Sharing Market. The report studies factors such as company size, market share, market growth, revenue, production volume, and profits of the key players in the China Bike Sharing Market.
The report provides Porter's Five Force Model, which helps in designing the business strategies in the market. The report helps in identifying how many rivals are existing, who they are, and how their product quality is in the Market. The report also analyses if the China Bike Sharing Market is easy for a new player to gain a foothold in the market, do they enter or exit the market regularly if the market is dominated by a few players, etc.
The report also includes a PESTEL Analysis, which aids in the development of company strategies. Political variables help in figuring out how much a government can influence the Market. Economic variables aid in the analysis of economic performance drivers that have an impact on the Market. Understanding the impact of the surrounding environment and the influence of environmental concerns on the China Bike Sharing Market is aided by legal factors.
China Bike Sharing Market Scope:
|
China Bike Sharing Market |
|
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1.39 Bn. |
|
Market Size in 2032 |
USD 1.99 Bn. |
|
CAGR (2025-2032) |
4.62% |
|
Historic Data |
2019-2024 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Segment Scope |
By Model
|
|
By Model
|
|
|
|
By Sharing System
|
China Bike Sharing Market Players
- Didi Bike
- HelloBike
- Ofo
- Qingju Bike
- Meituan Bike
Frequently Asked Questions
Nanjing and Beijing region have the highest growth rate in the China Bike Sharing market
Didi, Qingju, Hellobike, Ofo and Meituan Bike are the key players in the China Bike Sharing market.
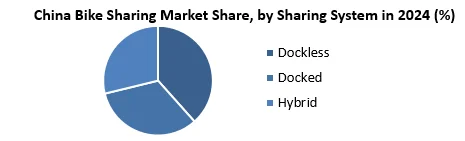
Dockless sharing system is dominating the regional market of China with market share of approximately 53.8% and YOY rate of 6.6%
1. China Bike Sharing Market: Research Methodology
1.1. Research Data
1.1.1. Secondary Data
1.1.2. Primary Data
1.2. Market Size Estimation
1.2.1. Bottom-Up Approach
1.2.2. Top-Up Approach
1.3. Market Breakdown and Data Triangulation
1.4. Research Assumption
2. China Bike Sharing Market Introduction
2.1. Study Assumption and Market Definition
2.2. Scope of the Study
2.3. Executive Summary
3. China Bike Sharing Market: Competitive Landscape
3.1. SMR Competition Matrix
3.2. Key Players Benchmarking
3.2.1. Company Name
3.2.2. Product Segment
3.2.3. End-user Segment
3.2.4. Revenue (2024)
3.2.5. Company Locations
3.3. Market Structure
3.3.1. Market Leaders
3.3.2. Market Followers
3.3.3. Emerging Players
3.4. Mergers and Acquisitions Details
4. China Bike Sharing Market: Dynamics
4.1. China Bike Sharing Market Trends
4.2. China Bike Sharing Market Dynamics
4.2.1. Drivers
4.2.2. Restraints
4.2.3. Opportunities
4.2.4. Challenges
4.3. PORTER’s Five Forces Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Technological Roadmap
4.6. Value Chain Analysis
4.7. Regulatory Landscape
5. China Bike Sharing Market: Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation (by Value in USD Million) (2024-2032)
5.1. China Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Bike Type (2024-2032)
5.1.1. PCB Connectors
5.1.2. Conventional bikes
5.2. China Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Model (2024-2032)
5.2.1. Free-floating
5.2.2. P2P
5.2.3. Station Based
5.3. China Bike Sharing Market Size and Forecast, by Sharing System (2024-2032)
5.3.1. Dockless
5.3.2. Docked
5.3.3. Hybrid
6. Company Profile: Key Players
6.1. Didi Bike
6.1.1. Company Overview
6.1.2. Business Portfolio
6.1.3. Financial Overview
6.1.4. SWOT Analysis
6.1.5. Strategic Analysis
6.1.6. Recent Developments
6.2. HelloBike
6.3. Ofo
6.4. Qingju Bike
6.5. Meituan Bike
7. Key Findings
8. Industry Recommendations
















